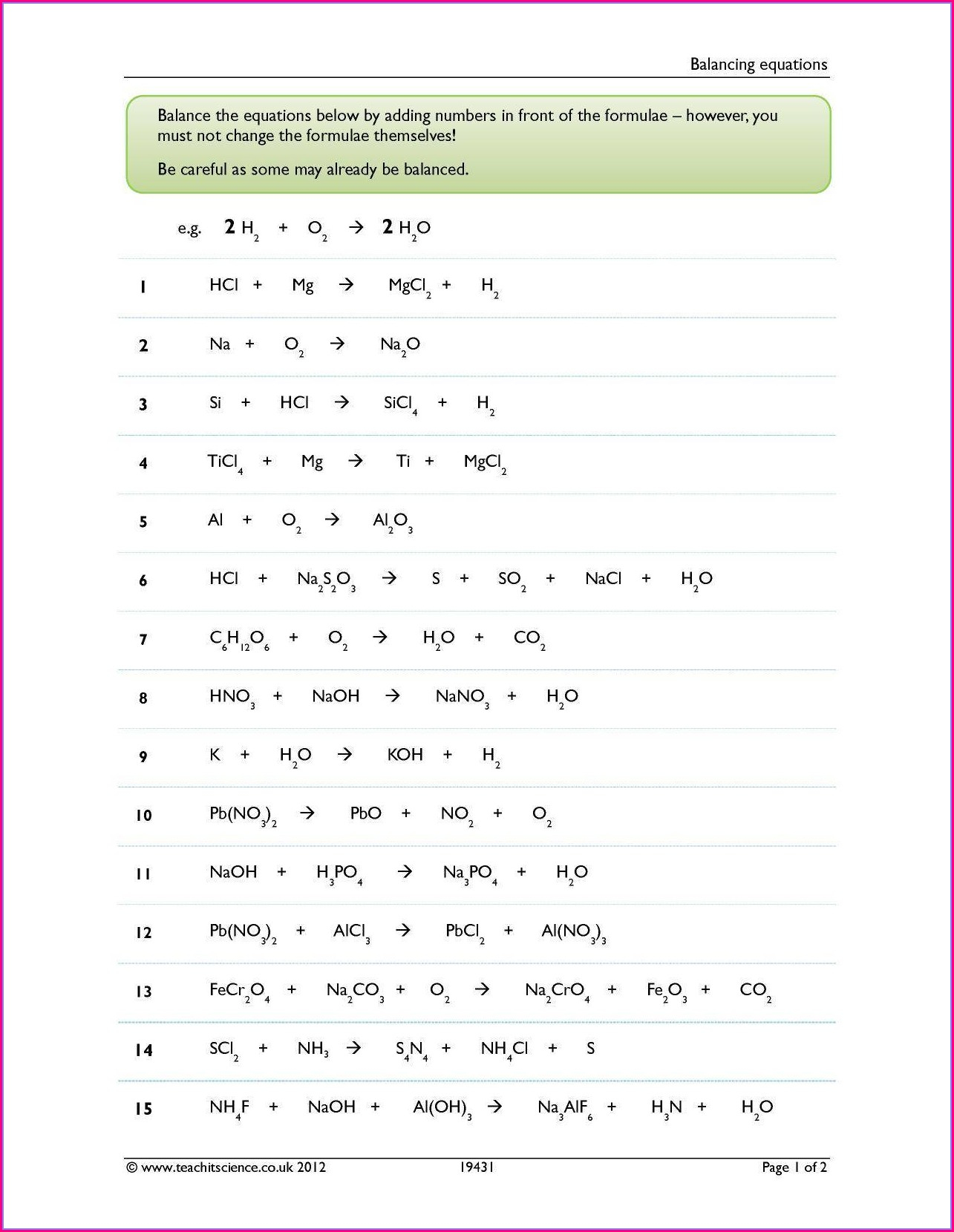
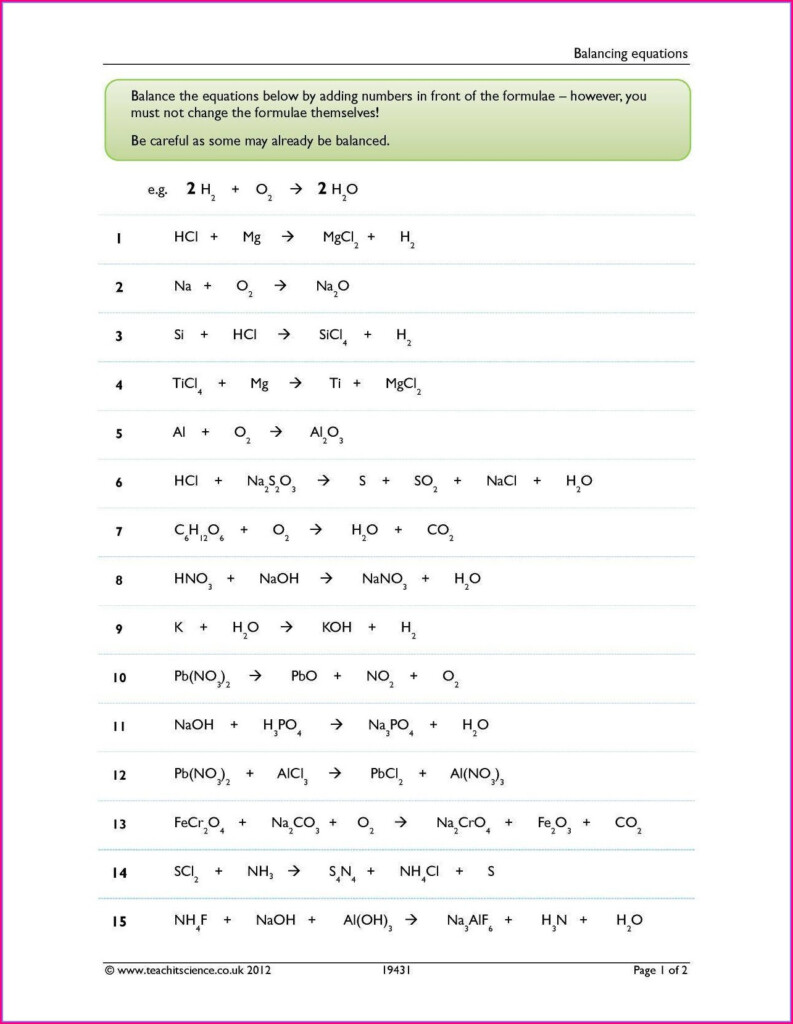
Chemistry Worksheet Chemical Equations Practice 1 – This Chemistry Equations Worksheet will help students understand the language of chemical equations. This worksheet should be completed after students have learned the rules of chemical formulae, bonding and state symbols, and enables teachers to provide feedback on where students may be lacking. The worksheet is divided into two parts. Page one summarizes the rules for writing chemical equations. Some of these rules may not be applicable to A Level students.
Chemical equations in balance
A chemical equation has two parts: a reactant and a product. The equation is separated by an arrow, so in the example below, the reactants are H2 and O2 and the products are H20 and CO2. Balance a chemical equation requires that the products and reactants must be equal. It can be hard to balance a chemical formula. However, there are ways around this.
A balancing chemical equations worksheet is available online to help students balance chemical equations. The worksheet includes ten unbalanced equations as well as an answer key. It is a great resource for elementary students learning about the chemical process. A student can complete the worksheet on their tablet and check their understanding with the answer key provided.
A balancing Chemical Equations worksheet is a visual activity that helps students to understand the differences between coefficients and subscripts when they are learning about balancing. This worksheet explains why balance chemical equations is so important and how it can be done. A balancing chemical equations worksheet allows you to easily create multiple worksheets. Each worksheet contains a matching answer sheet.
When you are learning about chemical equations, you have to understand the Law of Conservation of Mass. The Law of Conservation of Mass says that both sides of a chemical equation must have equal numbers of atoms. First, find an element with a single reactant or one product to balance a chemical equation. Next, you can use this element as a balancer for the first.
Classify reactions
A chemistry equation is a mathematical formula that describes a chemical reaction. Magnesium reacts with oxygen gas in order to make a solid magnesium oxide. Calcium metal reacts to water to create calcium hydroxide precipitate. When nitrogen reacts with hydrogen gas, ammonia is formed. The reaction does not destroy ammonia, which is unlike other chemical reactions. Therefore, the atoms are unaltered.
Chemical reactions are common everyday processes. These processes change the chemical structure of reactants and produce new substances. These reactions cause changes in the bonds structures of substances. The changes can involve energy use or release, and many physical indicators can be observed. These characteristics help classify reactions.
The common chemical reaction acid-base is found in nature. Both reactants exchange electrons. When an acid reacts with a base, it neutralizes the acid. In addition, an acid and a base can react with each other to form a new substance. Similarly, a precipitation reaction is a reaction in which the reactants disperse in a liquid. Different precipitates may be formed depending on the solubility of the reactants. There are also redox reactions, which involve the transfer of electrons between two or more reactants and result in ionic products. In addition, hydrolysis reactions use water as one of the reactants. They produce smaller products such as CO and H2.
Calculate coefficients
To solve chemical equations, the first step is to find the coefficients. The coefficients are whole numbers that represent the amount of each element in a chemical equation. They are calculated by balancing the numbers of the atoms on either side of the equation. For example, if a chemical has 10 atoms of oxygen and one atom of sulfur, the coefficient for oxygen would be 2. If the atoms on the opposite side of the equation have the same number, they are said to be a mixed compound.
You must correctly write reactants and products in order to balance chemical equations. In addition, you should also indicate the state of the substances with the help of symbols. For example, if the substance is a salt, it should be written NaCl. It cannot be written as Na2Cl2.
Next, we need to balance the atoms with the molecules in order to solve chemistry equations. We all know that the chemical equations must have equal amounts of both substances. Chemical equations must also be balanced, as each type of atom must be represented equally.
To determine the molar mass for a given element, you can use stoichiometric relationships to solve a chemical problem. By calculating the molar mass, you can convert Fe(s) into H2(g). The molar mass for H2O, for example, is twice that of a single H-atom.