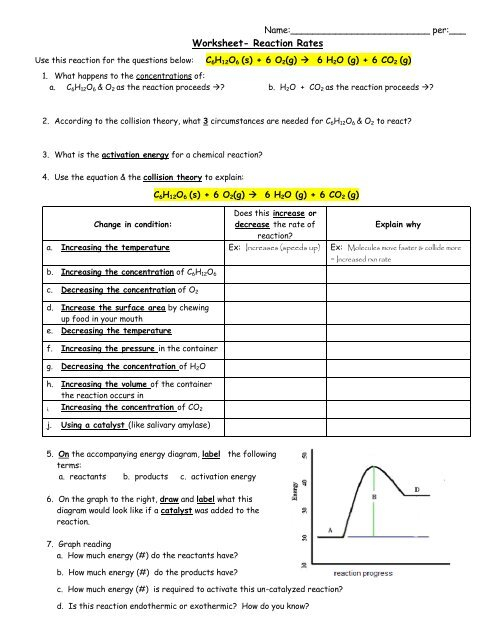
Chemistry A Study Of Matter Worksheet Reaction Rates – A Chemistry Reactions Worksheet is a useful tool to teach students the concepts of chemical change. Chemical reactions involve the transfer of energy among reactants and products. This type of change is either irreversible or reversible. This happens when two molecules or atoms react to create a new product.
Chemical reactions are caused by changes in bond structure
Chemical reactions are the process of creating new molecules by breaking or forming bonds between substances. These reactions are energy-intensive because energy is required to break bonds and then be released in a product. Different types of bond structures produce different amounts energy. A Lewis acid-base reaction, for example, produces a covalent bonds, in which the Lewis acid provides an electron pair, and the Lewis base receives one.
The energy involved in chemical reactions can be approximated using the bond strengths of reactants and products. The chemical reactions can cause these bond strengths to change. This energy can be measured in terms of heat, enthalpy and thermal energy. Potential energy is another way to express the energy of chemical reactions at the atomic level. This idea of energy is not often explained in chemistry textbooks.
They involve the transfer of energy between reactants and products
Chemical reactions involve energy being transferred from reactants into products. The form of bonds is how the energy is transferred. Bond energy, also known as bond energy, is measured in kJ*mol$-1. The amount of energy that can be transferred in a chemical reaction depends on the amount of energy that the reactants and products have.
Understanding chemical reactions is key to understanding how energy is transferred. These reactions are known as energy change. This is energy absorption or release that occurs when chemical bonds break. This energy can be either heat or light depending on the products and reactants. The energy transfer occurs because of the differences in stored chemical energy, or enthalpy.
They are reversible
Reversible reactions are when both reactants and products are converted to each other in a chemical reaction. It occurs when the conversion of the reactants to the products occurs simultaneously. This is one of the most common reactions in chemistry. Here’s how it works.
A reaction that occurs between a substance and a gas can be reversible or irreversible. For instance, if an acid reacts with an alcohol, the result is a new compound, which is called a product. In order for this reaction to occur, the gas molecules that were previously bound to the solution must be released. A Dean-Stark apparatus is used to separate the reactants, ensuring that the desired product is produced.
They are irreversible
Chemistry can produce many different types of reactions. Reactants and their surroundings will determine the type of reaction. Most chemical reactions are irreversible. These reactions involve the conversion of multiple reactants into one or several products. Sometimes the catalyst can be used to enhance the reaction.
Reversible reactions are those that occur in closed containers. Ammonium chloride, for example, can be heated to make ammonia or hydrogen chloride. It is then converted to ammonium chloride when it cools. These two reactants will then recombine.
They involve redox reactions
Redox reactions involve the transfer of electrons between different chemical species. The oxidation process results in the loss of one or several electrons by an oxidizing agent, while the reduction process results in the gain of electrons from the reducing agent. Redox reactions can affect a variety of environmental variables, including contaminant mobility and degradation. For example, hexavalent chromium is highly toxic when oxidized. Trivalent chromium, on the other hand, is less toxic and less mobile. Likewise, arsenic, uranium, and selenium are less mobile under oxidizing conditions.
Redox reactions can also occur during decomposition processes. This results in a smaller chemical compound. For example, if CaCO3 reacts with CO2, it will decompose into CaO and CO2, but the oxidizing agent gains an electron. An oxidizing agent can also gain oxygen and bring it into the molecule. Typical oxidative reactions in organic chemistry include dealkylation, epoxidation, aromatic ring cleavage, and hydroxylation.
They involve acids and bases
A Chemistry reaction involves acids and bases reacting with each other to produce a new substance. A salt is a substance that forms when an acid reacts with a base. Salts are crystal substances that dissolve in water. They can also be bitter. There are many theories as to how acids and bases interact with one another.
Both acids and bases play important roles in chemical reactions and in daily life. The body’s acidity helps to maintain a stable internal environment. Acidity is also important in baking cakes. The acidity of a lake determines whether it can sustain aquatic life. As a result, a large percentage of chemical processes involve either acids or bases. Acids and bases also play a key role in biological processes. The pH and alkalinity in the soil and water are crucial for animals and plants. As such, the chemistry of acids and bases is ubiquitous and permeates our daily lives.