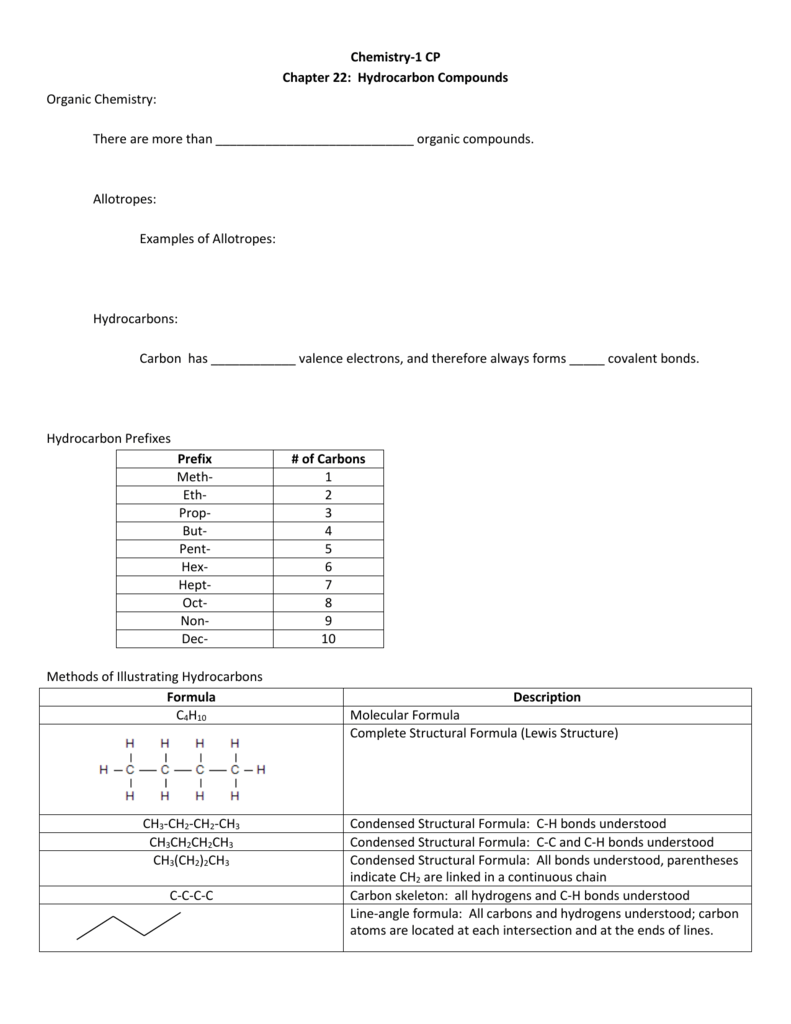
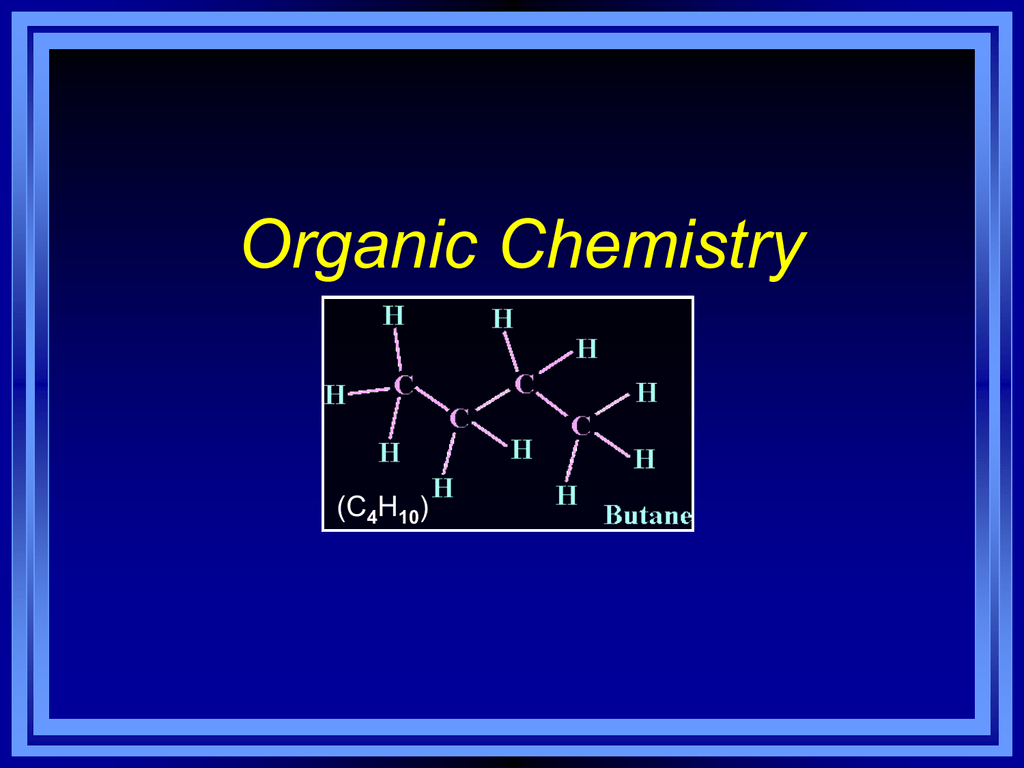
Chemistry Chapter 22 Hydrocarbon Compounds Worksheet – Students can use this Chapter Chemistry Worksheet to reinforce their knowledge of the subject. In the chemical reaction of potassium chlorate, oxygen is absorbed and potassium chloride is released. As chemical bonds are broken, this reaction releases energy. However, mass is conserved in this reaction. The reaction conditions are explained in the chemical equations. It is also clear whether the energy is conserved or evolved.
AP Chemistry instruction activity
Students may find AP Chemistry difficult to master. Therefore, many students seek additional help outside of class. Identify which students are in need of extra help and set aside time after school to work with them. Both the teacher as well as students will benefit from this approach. In addition, students can develop a better understanding of the material they will be studying.
Integrating AP-specific science practices in the classroom is a great way to engage students. To help students learn the science behind chemistry, teachers can use a practice lab activity. This includes reporting laboratory findings and laboratory investigations. Students will appreciate this activity because it is focused on one area at a given time. This can help reduce frustration and stress.
The redesign of the AP Chemistry curriculum has created new challenges for teachers, as well as students. The exam has new formats and content, which has impacted how students learn. Teachers also need time to adjust their teaching practices to the new standards. Future research should focus on the characteristics of those teachers who were most affected by this curriculum reform in order to assess its effects.
An example AP Chemistry curriculum is one option. The AP curriculum has a variety of examples for teachers and students to review. The AP curriculum is based on the standards of the College Board. Each unit contains links to helpful resources and activities. The materials include videos, simulations, and other forms of formative assessment.
Reduced form of reducing agent
The reduction of an element is a chemical process that involves transferring an electron from one atom to another. There are many ways that the reaction can occur. In the simplest case, the reducing agent is the same element that is being oxidized. In other cases, the reducing agent is a different element. In both cases, the compound must contain an element in a lower state of oxidation than the oxidizing elements. The oxidizing element loses electrons, and the compound becomes reduced. An example of a reducing agent is sulfur. SO32’s sulfur atom is in a +4 state of oxidation and can be oxidized to +6.
Reducing agents include most organometallic compounds. Cuprous, chromium and sodium are the strongest reducing agents. Chloride is the weakest reducing agent. Both the oxidising as well as reducing forms have similar results. It is therefore important to choose the right reducing agent for your sample.
Carbon monoxide is another type of reducing agent. This gas is able to reduce many metallic oxides back to their original metal form. Many metallic salts can also be reduced to metals by this gas. For example, hydrogen gas can reduce palladium chloride to palladium metal.